1
/
of
1
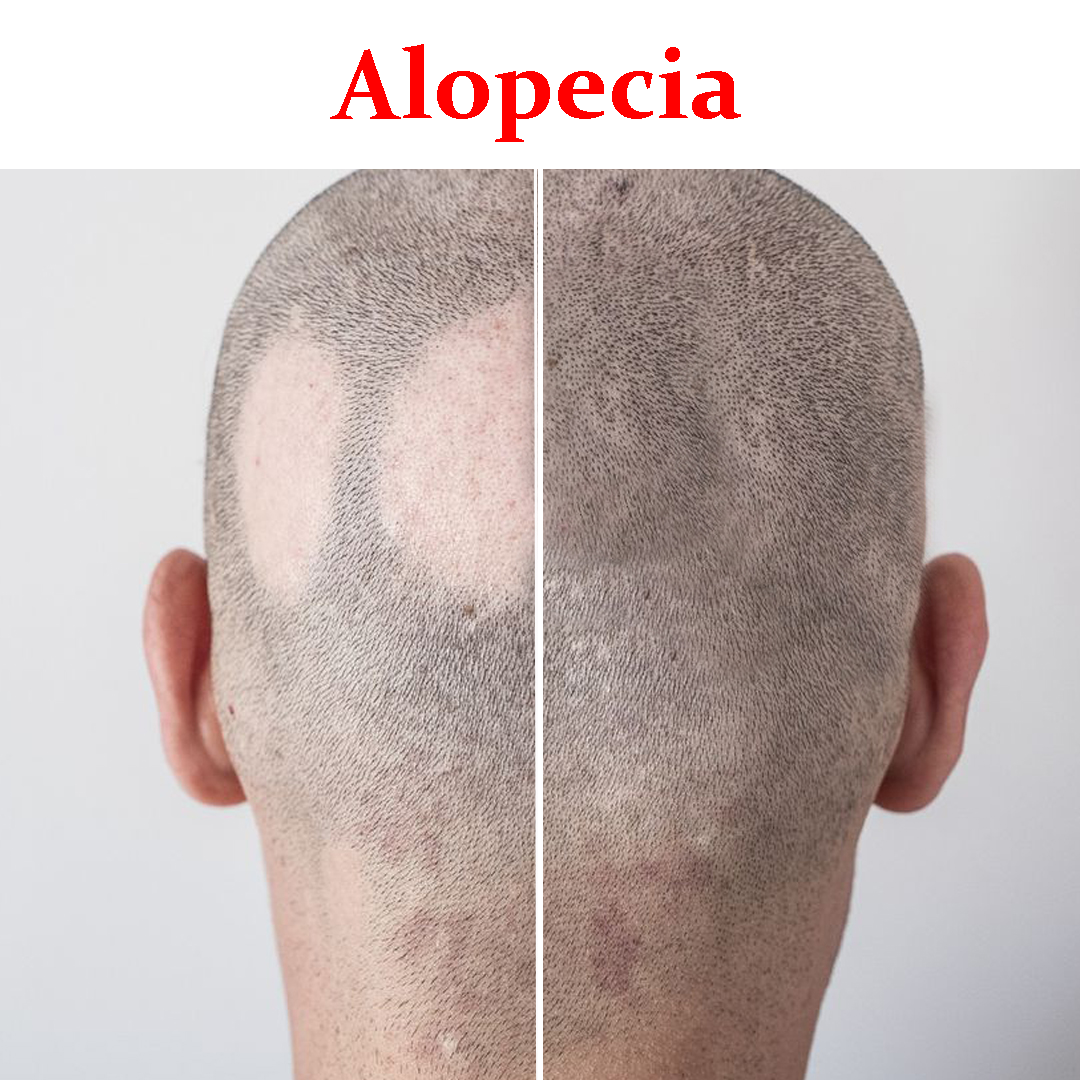
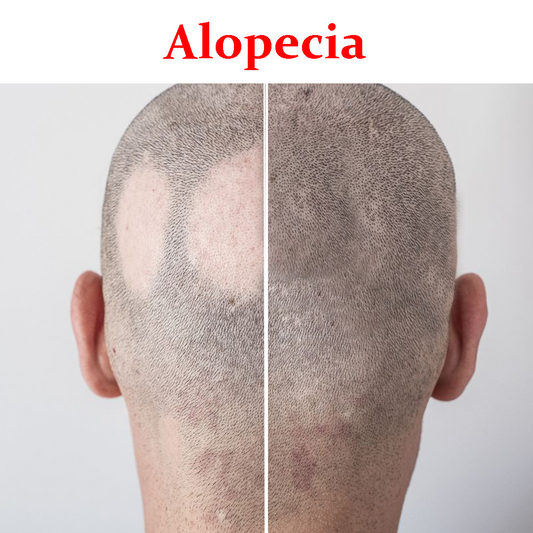
Aloepecia- Product Box
Aloepecia- Product Box
Regular price
Rs. 3,000.00
Regular price
Rs. 3,000.00
Sale price
Rs. 3,000.00
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Couldn't load pickup availability
Description
Alopecia areata is an issue that happens when the immune system attacks hair follicles and causes hair loss. Hair follicles are the structures in skin that form hair. While hair can be lost from any part of the body, alopecia areata usually affects the head and face.
Who Gets Alopecia Areata?
Anyone can have alopecia areata. Men and women get it equally, and it affects all racial and ethnic groups. The onset can be at any age, but most people get it in their teens, twenties, or thirties. When it occurs in children younger than age 10, it tends to be more extensive and progressive.
Types of Alopecia Areata
There are three main types of alopecia areata:
- Patchy alopecia areata. In this type, which is the most common, hair loss happens in one or more coin-sized patches on the scalp or other parts of the body.
- Alopecia totalis. People with this type lose all or nearly all of the hair on their scalp.
- Alopecia universalis. In this type, which is rare, there is a complete or nearly complete loss of hair on the scalp, face, and rest of the body.
What comes in the Product Box?
- Related Herbal Supplement
- Ointment for day application
- Ointment for night application
- immunity booster nutrition
- Diet Chart (4 Weeks)

Products/Medicines related to Other Hair Concerns
-
Deep Hair Line- Product Box
Regular price From Rs. 4,732.00Regular priceRs. 4,384.00Sale price From Rs. 4,732.00 -
Hairloss- Product Box
Regular price From Rs. 3,887.00Regular priceRs. 2,875.00Sale price From Rs. 3,887.00 -
Dandruff- Product Box
Regular price From Rs. 2,761.00Regular priceRs. 2,310.00Sale price From Rs. 2,761.00 -
Aloepecia- Product Box
Regular price From Rs. 3,000.00Regular priceRs. 3,000.00Sale price From Rs. 3,000.00